Gartner's Toolkit for AI Use Case Evaluation
A reader's perspective on the utility of Gartner's AI framework for evaluating AI Use Cases and identifying a shortlist for Product Development
While exploring Gartner resources, I came across a framework that can be highly valuable for mapping multiple use cases and analyzing their business benefits in terms of business value and feasibility. Here are my key takeaways from studying the framework, based on the literature available on Gartner's website.
Where to use this model approach
The framework is useful for conducting use case evaluation workshops that involve a combination of business and technical stakeholders (IT and AI) within the relevant business organization. The model helps different teams come together to evaluate multiple business cases in an initial lightweight discussion, with the goal of prioritizing and shortlisting an initial set of use cases for formal product development.
How to use this model during discussions
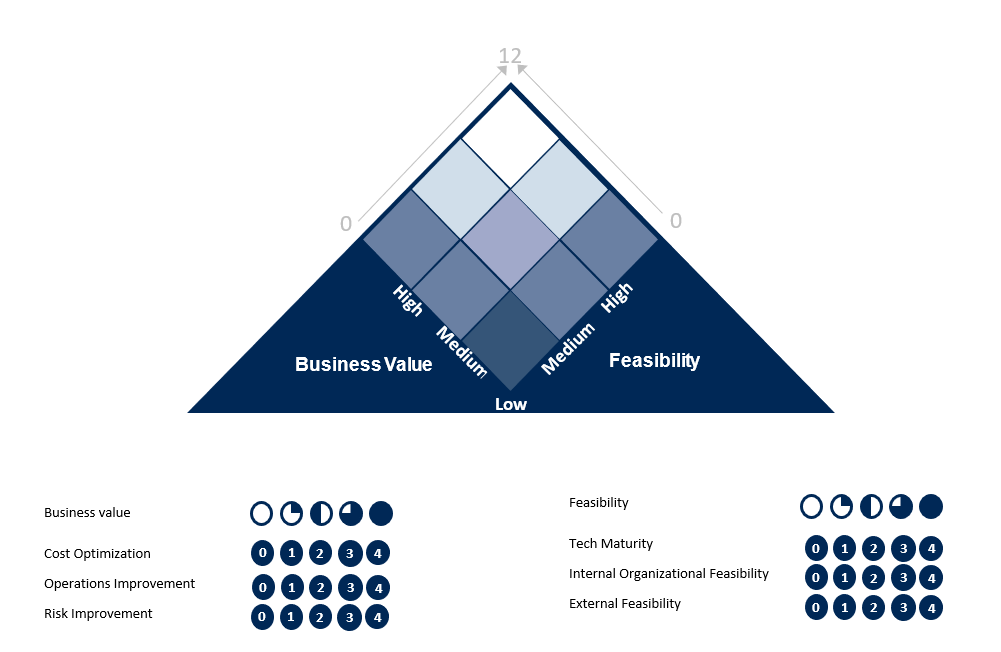
Business Value Evaluation
Business Value evaluation is primarily considered basis the three main criteria -
Rate of improvement in Cost Optimization
Rate of improvement in Operations Excellence (Operations Improvement)
Rate of Risk Improvement (Risk Reduction)
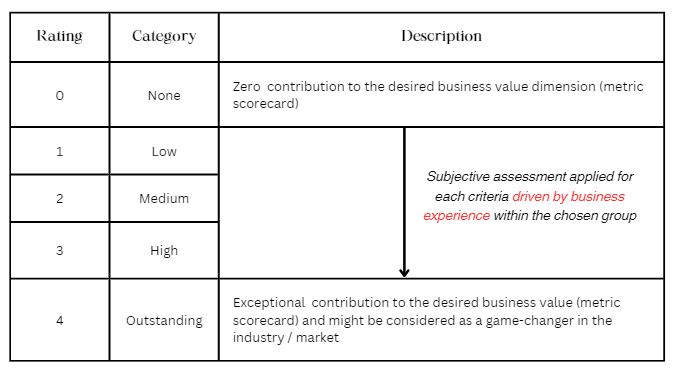
All the above criteria are pegged to a desired (or most desired) business value like market growth, revenue growth or any business KPIs that are considered as part of the business scorecard within the organization. Each criteria is discussed during the initial lightweight discussion and a consensus is arrived within the group to rate the contribution on a scale of 0 to 4.
Choosing the right business driver and reaching a consensus-driven rating is a qualitative approach that should be effectively managed within the organization.
In the realm of business management, qualitative approaches can sometimes be prone to getting caught up in lengthy debates. As experienced business managers and leaders, it is paramount for business opportunity managers to skillfully navigate these discussions in order to reach timely resolutions.
Feasibility Evaluation
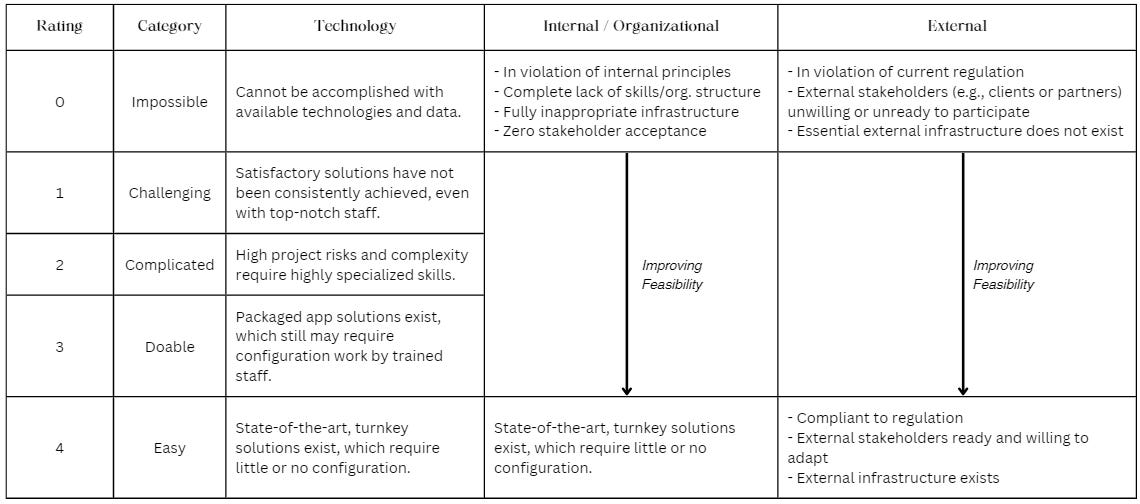
Feasibility evaluation considers three main criteria for assessing the overall technical feasibility as listed below -
Technology Maturity
Internal Organizational Feasibility - Primarily covers softer elements within the business encompassing adoption attitudes, leadership buy-in, in-house skillsets, and a few others.
External Organizational Feasibility - Primarily considers factors influencing technology adoption examining societal outlook on technology adoption, influence of peer adoption, and impact of government regulations on the adoption of technology.
Barring technology maturity, the other factors are highly subjective, and the assessment of these factors can vary from person to person and even from region to region. This variability makes it challenging to apply them on a pan-organizational level.
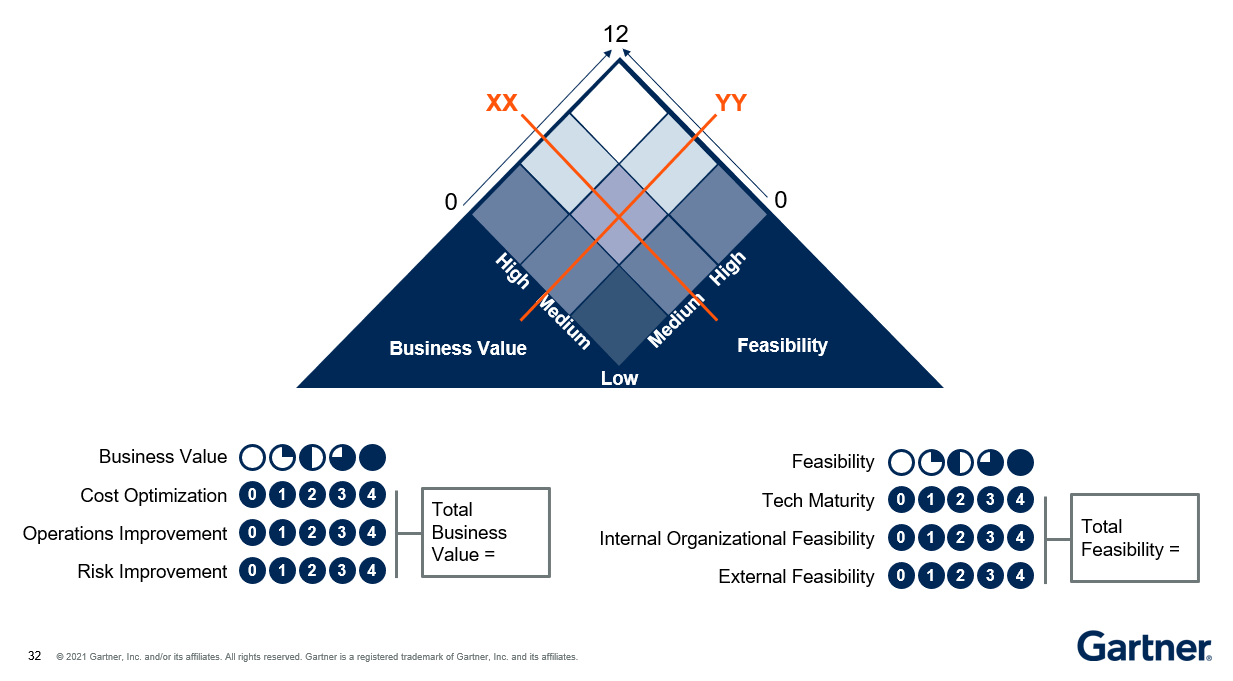
Prioritizing Opportunities
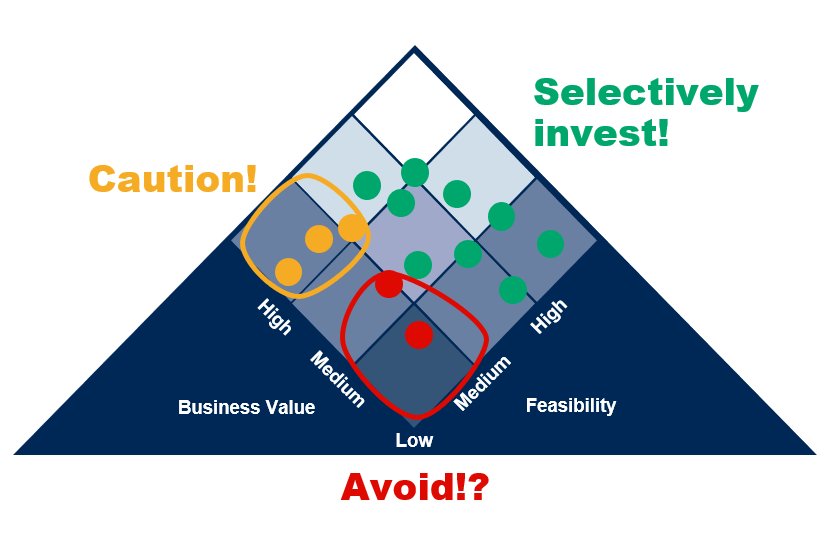
The scores for all the above-mentioned criteria are summed up under business value and technical feasibility separately. The various opportunities are plotted on a grid, with the above-mentioned categories serving as the axes.
Plotting the opportunities in the grid visual as above helps the organization prioritize ideas or opportunities that have a higher probability of success.
Conclusion
Conversation-Starter 💡 — The shared framework provides a strong framework to initiate conversations within decision-making group in the organization or classes of business (in very large organizations).
High subjectivity ⛔ — High amount of subjectivity involved in assessing criteria especially linked to organizational feasibility and the external environment.
Overall, the framework provides an interesting perspective and does help to kickstart the groundwork in terms of evaluating prospective use cases but, would require a reasonable amount of human expertise while evaluating the subjective criteria linked to the overall prism framework.
References
Whit, Andrews, and Barot Soyeb . “Toolkit: Use This Worksheet to Frame AI Use Cases in Executive Meetings.” https://www.gartner.com, Jan. 2023, www.gartner.com/document/4004557?ref=lib.